
How to Become an EMT ~ Step by Step
Becoming an EMT (or Paramedic) typically involves several steps. It is important to note though, that every person's journey is a bit different, so these steps should serve as a guideline to help you personalize your own journey.
- Understand what an EMT is, and what the difference is between an EMT and Paramedic
- Understand the education requirements
- Understand certification requirements
- Decide if your personal aptitude and skills are a good fit for the job
- Obtain the education or training you need
- Understand the job market and what you might need to know to land a job
What is an EMT? What is the Difference Between an EMT and Paramedic?
EMTs and Paramedics care for injured or sick individuals in emergency situations. They respond to 911 calls for emergency medical assistance, evaluate an individual’s injuries and administer treatment such as drugs, and diagnostic procedures such as stomach suction, heart monitoring or airway management. They may also possibly bring them to a hospital for further treatment.EMTs are
If you are like most people, you probably use the words EMT and Paramedic interchangeably. This is incorrect! There are differences between EMTs and Paramedics:
| EMTs | Paramedics |
| Courses typically are around 120-150 hours of training | Training that requires anywhere from 1,200 to 1,800 hours |
| Able to administer CPR, administer glucose to diabetics, give patients oxygen, treat asthma attacks and treat those having major allergic reactions | Everything EMTs can do PLUS provide any treatments that involve breaking the skin, such as administering needles |
| Provide advanced airway management for patients | |
| Administer medications | |
| Start intravenous lines | |
| Provide resuscitation to those that have had heart attacks and other traumas |
Education Requirements for EMTs and Paramedics
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, a postsecondary education program is generally required to pursue a career as an EMT or paramedic. You might take courses in a non-degree program, which may take a year or two, or earn an associate degree. These programs may be available at technical schools, community colleges, and emergency care training institutes. You’ll need to have earned a high school diploma or the equivalent, and many programs may also require you to have cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) certification.
Keep in mind that EMTs and paramedics may have different educational requirements. EMT-level programs may cover the following subjects:
- Assessing a patient’s condition
- Handling trauma and cardiac emergencies
- Clearing obstructed airways
- How to properly use field equipment
- Handling emergencies
Advanced EMT-level programs may cover additional areas, like:
- Using complex airway devices
- Administering intravenous fluids
- Giving medications
Paramedics must complete EMT and Advanced EMT levels of instruction, along with additional, advanced courses that may require about 1,200 hours of instruction. Some paramedics may earn an associate’s degree. In addition to all of the above, paramedics may learn:
- Advanced medical skills
- Stitching wounds
- Administering intravenous medications
An EMT or Paramedic's Salary Potential
- Lowest 10th%
$23,490 - Median
$35,400 - Highest 90th%
$59,860
States with the Highest Employment Levels
| STATES | 2019 ANNUAL MEAN WAGE | NUMBER OF JOBS |
|---|---|---|
| California | $43,680 | 21,990 |
| Texas | $37,000 | 19,380 |
| New York | $44,920 | 18,610 |
| Pennsylvania | $34,310 | 13,890 |
| Florida | $36,190 | 11,790 |
How Do Your Skills Stack Up?
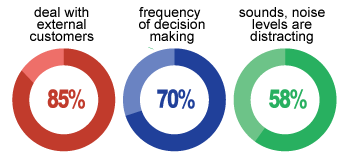
As reported by O*NET, these types of tasks are conducted every day in this role – would you feel comfortable performing these tasks as part of the day to day life of an EMT or Paramedic?
What Will You Learn with an Associate – Paramedic Technology Degree?
Associate degree programs for paramedics help prepare future emergency medical technology professionals for handling this challenging role. You could learn how to assess patients in an emergency, medically intervene to save a patient’s life, and keep patients safe and cared for while they are being transported to emergency medical facilities. You may also pursue “soft” skills, like how to communicate effectively and compassionately with patients and their family members during an emergency. And the program may offer students the chance to pursue clinical or field experience. Here are a few potential courses you might take::
- Critical trauma care
- Cardiac life support
- Human biology
- Intro to psychology
- Pediatric care
- And more!
EMT and Paramedic Education: The Breakdown
Wondering how much education EMTs and paramedics typically pursue? Here are the stats, according to O*NET:
| Post-secondary certificate - 43% of respondents |
| Some college but no degree - 30% of respondents |
| Associate degree - 12% of respondents |
FAQs About How to Become an EMT or Paramedic
What is the average EMT or Paramedic salary?
Do EMTs and Paramedics need to be licensed or certified?
What job titles are similar or the same as an EMT?
What are common types of software I would have to learn as an EMT or Paramedic?
What does the EMT job market look like?
Interesting Facts about EMTs and Paramedics
Here are a list of Fast Facts as stated by the National Registry of Emergency Medical Technicians
- There are four nationally defined levels of EMS Professionals: Emergency Medical Responder(EMR), Emergency Medical Technician(EMT), Advanced EMT (AEMT), and Paramedic. Some States may use different titles and many have additional licensure levels.
- 75% of nationally certified EMS professionals are male, 85% are of non-minority status and 45% have a college degree or higher.
- Over 55% of nationally certified EMS professionals reported having participated in a multi-agency disaster drill that included biological, chemical or nuclear scenarios within the past 24 months.
- EMS treats approximately 25-30 million patients per year with estimated annual expenditures of about $5 billion.
Job information sourced from O*NET
