
The Basics of Becoming a High School Teacher
Are you investigating how to become a High School Teacher? The main job of a High School Teacher is to instruct (through lessons and discussions) students at the secondary level in public or private schools. They typically teach in one or more subjects such as English, mathematics, or science.
Among others, day to day activities would include planning lessons, grading assignments, and communicating with parents about student’s progress. High School Teachers also help students develop skills that will be needed to attend college or enter the job market.
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, all states require High School Teachers in public schools to have a bachelor’s degree. Some states also require that the teach major in the field they want to teach, such as math or chemistry. In addition to the bachelor’s degree, some states also require that teachers in public schools also earn a master’s degree. Private school teachers do not need to follow state guidelines, however, private schools also typically seek High School Teachers who have a bachelor’s degree. What general knowledge should someone in this career possess? High school teachers should be knowledgeable in creating curriculums, instruction and teaching, and learning strategies. It is also important to be able to: act as a good mentor; identify educational needs of students; and communicate in a way that is easily understood.
A High School Teacher's Salary Potential
- Lowest 10th%
$40,540 - Median
$61,660 - Highest 90th%
$99,660
States with the Highest Employment Levels
| STATES | 2019 ANNUAL MEAN WAGE | NUMBER OF JOBS |
|---|---|---|
| California | $85,080 | 109,840 |
| Texas | $58,000 | 107,190 |
| New York | $87,240 | 75,360 |
| Florida | $57,880 | 50,640 |
| Ohio | $64,410 | 47,510 |
How Do Your Skills Stack Up?
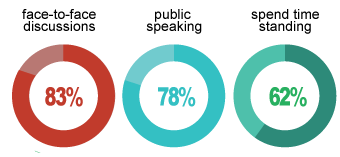
As reported by O*NET, these types of tasks are conducted every day – would you feel comfortable performing these tasks as part of the day to day life of a High School Teacher?
What Will You Learn with a Secondary Education Degree?
A degree in secondary education will typically cover coursework like:
- Teacher Leadership in Secondary Education
- Instructional Technology
- Assessment
- School and Family Partnerships
- Educational Change Processes
A degree in secondary education is usually designed to help future teachers prepare for the challenges of leading a classroom and influencing their learning communities for the better. Coursework might feature principles of teacher and school leadership, educational changes and technology, school safety, student assessment, and other important topics. Of course, coursework for a prospective secondary education teacher is aimed at the needs and challenges of secondary education specifically, with a focus on classroom practices, principles, and activities best-suited to students in this category.
Interesting Facts about Teachers
According to the National Center for Education Statistics (NCES), 2012 Staffing Survey, identified a number of trends in the teaching profession, some of these include:
- 58% percent of public high school teachers were female, and 42% male.
- 44% of teachers were under age 40.
- 56% of public school teachers had a masters or higher degree, while 43% of private school teachers had a master's or higher degree.
- The average class size for public High school teachers of self-contained classes was 18 students.
- 99% of Public School Teachers participated in some type of Professional Development the previous 12 months.
FAQs About How to Become a High School Teacher
What is the average High School Teacher salary?
Do High School Teachers need to be licensed?
How many high schools are there in the U.S.?
What job titles are similar or the same as a High School Teacher?
What are common types of software I would have to learn as a High School Teacher?
What types of professional organizations may teachers be interested in?
Job information sourced from O*NET
